*Written for Interactions magazine by Hugh Dubberly.*
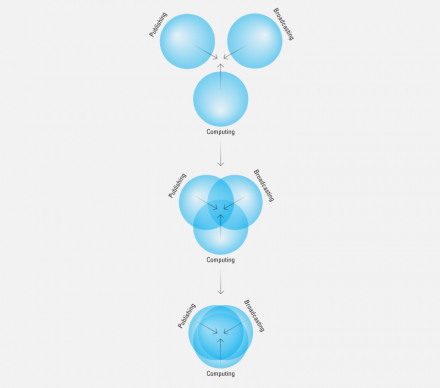
In 1980, when I was a college student, I heard Nicholas Negroponte speak about the future of computing. What stood out most was his model of convergence. Negroponte presented the model in three steps. The first slide showed the publishing, broadcasting, and computing industries as separate rings; the second slide showed the rings beginning to overlap; and the third slide showed the rings almost completely overlapped. The publishing, broadcasting, and computing industries were converging and would soon become one.
Convergence 1.0 = Publishing + Broadcasting + Computing.
Convergence has become shorthand for a series of arguments. First, all media will become digital. Second, the analog-to-digital transition will transform media production and distribution, creating opportunities and disrupting existing businesses. And third, and perhaps less obvious in 1980, once media are digital, boundaries between media types will blur and opportunities for interaction will grow, creating new ways for us to make arguments, explain ideas, and tell stories.
In many ways, Apple’s iPad fulfills Negroponte’s prediction; iPad is the first platform to bring together rich media, interactivity, portability, and broad distribution. Paul Saffo tell us that new technologies require about 30 years to move from the lab to consumers’ hands.[1] So: convergence has arrived right on schedule.
Negroponte’s model of convergence has helped me make sense of changes in the computer industry since I was a student. Today, however, the original model is no longer sufficient to describe the emerging world of networked, mobile applications. We need to revise the model.
The internet is becoming a sort of operating system, providing networked *services* to applications; online *social* networks are evolving into communications and identity platforms; and boundaries between the virtual world and the *physical* world are increasingly blurred. These changes are not independent; they are connected and mutually reinforcing. Service, social, and physical are converging.
Convergence 2.0 = Service + Social + Physical.
Convergence 2.0 builds on Convergence 1.0 and helps explain the new types of businesses now emerging. Convergence 2.0 also provides a framework for planning and designing applications adapted to the new environment.
The value of these models (like all models) lies in their ability to explain what’s happening and predict what might happen (or generate options). Value accrues at two scales. The models suggest large-scale changes to industries, e.g., the “death” of silver-halide photography and offset lithography. The models also suggest changes for individual businesses and products, e.g., designers can use the models as frameworks for thinking about new applications.
**Convergence 1.0**
Convergence gained visibility in the late 1980s and early 1990s, as end-user authoring tools HyperCard and Director led to a boom in “interactive multimedia titles”. Adventurous publishers distributed CD-ROMs (limited to 700 MB of data) through bookstores, but they had no mechanism for previewing, aside from screenshots on the packages.
The web emerged a few years later, offering more efficient distribution and easy sampling. At first, the web was a major step backward from multimedia, a step backward into the mostly-text, not-very-interactive world of HTML1. Over fifteen years, the web caught up. Bandwidth increased; streaming video became viable; and JavaScript and the DOM (document object model) matured. Coupled with mobile devices, such as iPad, the web now provides a convenient way to deliver interactive multimedia.
What else changed during convergence?
Convergence 1.0 = Publishing + Broadcasting + Computing. In 1980, Nicholas Negroponte described the impending convergence of these industries.
**Publishing + Computing**
Mechanical typesetting became digital; digital typesetting became electronic publishing. The Macintosh, PageMaker, and LaserWriter gave birth to desktop publishing. As desktop publishing tools improved, direct-to-plate publishing became possible. Now, mass-produced lithography is being replaced by mass-customized ink-jet printing.
“Mass” is being replaced by “self” with print-on-demand services like Blurb and Lulu for books and Shutterfly, Snapfish, and the Kodak Gallery for photos. (Kodak is a cautionary tale, an early innovator in digital photography that failed to adapt its core business fast enough to remain relevant.)
Print-on-demand isn’t limited to books and photos; it also includes t-shirt and tchotchke printing services like Zazzle and CafePress. Brian Mathews, Vice President of Autodesk Labs, predicts that the scan-edit-print paradigm of two dimensions will soon expand to three dimensions with on-demand 3D printing and even home fabrication of complex products.
**Broadcasting + Computing**
Negroponte used broadcasting as a metaphor, a part standing for the larger whole of the music, television, and film production and distribution industries.
Like publishing, filmmaking is becoming digital. Commercial animation is now produced almost entirely with digital tools. And “live action” is regularly merged with digital effects. Human actors have begun to act through or even inside “digital puppets”. Movie theaters are converting from celluloid projection to digital projection.
The convergence of broadcasting and computing includes not only content but also devices—the convergence of consumer electronics and computing. Music players, cameras, phones, and TVs have all become computers. Apple dropped computer from its name while turning itself into a consumer electronics company. The battle for control of the living room has begun.
Distribution has changed, too. First VCRs and then TiVo and other DVRs enabled time shifting and ended the tyranny of broadcast scheduling. VHS and Blockbuster gave way to DVDs and NetFlix. Cable became another means of delivering digital content.
Along the way, video moved online and became “on-demand”. In 2005, YouTube stuffed dancing cat videos into Flash files and embedded them into web pages. Netflix reinvented itself as a streaming video service, followed by Roku, Boxee, AppleTV, and Hulu. The TED Talks and Kahn Academy show the promise of amassing libraries of educational videos. A9’s Block View and Google’s Street View recreated the Aspen Movie Map[2] around the world.
An early sign of the convergence of broadcasting and computing was the video game.
Video games have become a $10.5 billion per year business in the US, rivaling the movie industry’s $10.6 billion annual revenue.[3] The two industries are closely intertwined. Disney regularly turns films into games. Harry Potter has spawned hundreds of games. Some movies have adopted aspects of games, and an animation genre, Machinima, has emerged using video games to produce movies.
Video games have affected culture more broadly. Gamification—including game play or game principles in applications and services—has become a way to increase user engagement and has spawned articles, books, and conferences.
**Publishing + Broadcasting**
Shipping atoms costs more than shipping bits. Printing of newspapers, magazines, and academic journals may largely disappear. Last September, Arthur Sulzberger, publisher of the New York Times, acknowledged, “we will stop printing” as the paper reinvents itself online.[4] [5] In May, Amazon reported “selling more Kindle books than print books . . . hardcover and paperback—combined.”[6]
RSS has disaggregated publishing, and created opportunities for re-aggregators like Google News and Popurls and for attention analyzers like Flipboard, Pulse, and Zite. At the same time, thousands of new voices have sprung up in blogs, microblogs, and tweets.
Broadcast news services are also moving to the web and branching out. The BBC and CNN publish text stories. Meanwhile, the New York Times publishes slideshows with voice-overs and recently began publishing videos. (Newspapers have been slow to move into video, especially given how easy and inexpensive video has become to produce.)
**Convergence 2.0**
The rise of the internet requires a reassessment of Convergence 1.0. Negroponte developed his model of convergence very early. Personal computers were in their infancy. The internet was a small government experiment used mainly to exchange mail and files. Nothing like the web existed.
Negroponte has acknowledged, that none of us saw the web coming. It took a while to see, as Andy Grove later did, that “All companies will be internet companies, or they will be dead.”[7] Or as Tim Misner put it, “All hardware products want to be web-sites.”[8] Or that most human services will become networked. Or as Tim O’Reilly observed, “Virtually every application is a network application, relying on remote services to perform its function.”[9]
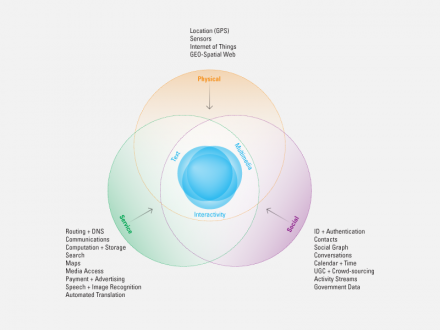
Convergence 2.0 recognizes that interactive multimedia exist within a networked world and depend on networked services. It recognizes that most services have a social component. And it recognizes that people are rooted in the physical world and networks are increasingly connected to things. Convergence 2.0 integrates interactive multimedia with internet-based services, social networks, and the physical world.
Convergence 2.0 = Service + Social + Physical. Combined with interactive multimedia, they provide a framework for understanding the emerging generation of network-based mobile applications.
**Services**
We often think of the internet as a network of networks. It’s that and more. The internet is also an emerging ecology of services. A network of networks requires interchanges, routing services, and other systems for directing traffic. DNS (the Domain Name Service) and its system of governance is an important and early example. Servers that implement protocols, such as FTP (file transfer), SMTP (email), HTTP (web), SMS (texting), and RSS (feeds) are a few of many examples of a growing infrastructure of network services.
Internet users have also come to depend on higher-level services, such as search, GPS, identification, authentication, and many more. Without networked services, interactive media would be less viable. Amazon’s WhisperNet, the wireless network that instantly delivers books to Kindle readers, is a key element in creating a seamless experience.
Some applications such as Google Maps and Facebook have turned themselves into platforms, publishing their APIs so that others can build on top of them.
A new class of network services is emerging. Services that identify context and gauge relevance—providing the right information and the right tools for the situation—are becoming important.
**Social**
Social networks are important in all cultures. Online social networks, such as Friendster, MySpace, Orkut, Linkedin, Facebook, and Twitter, tend to increase the probability of finding people with similar interests, the number of interactions between people, and the rate of communications between them.
But “social” is more than just online social networking sites. Wikipedia and its variants, Threadless (a crowded-sourced design service), and open-source software projects are social. Social has become a component in most networked services. Modern search algorithms, collaborative-filtering, and crowd-sourcing are all inherently social, relying on “the wisdom of crowds” to create value.
**Physical**
Of course, the physical world has been here all along; we’ve just taken a while to see how it will connect to form what Kevin Ashton calls “an internet of things”.
“Physical” means providing context:
– Where am I? What’s around me? Location—mapping and descriptions
– Who am I with? Participants—identity and relationship
– What are we doing? Activity—process and current stage
– Why are we doing this? Goals—intention and interest
– When is it happening? Time—calendar and commitments [10]
And “physical” means providing information—labels, summaries, meta-data, and deep descriptions—about the things around us so that we can understand our context.
“Physical” also means providing information from a network of sensors around us, on us, and in us—sensors measuring location, motion, energy use, temperature, humidity, and a wide range of biomarkers.
**Designing with Convergence 2.0 In Mind**
The convergence model also has practical value; it can help product managers and designers generate options. We can identify opportunities we might otherwise overlook by using the model as a sort of checklist.
How does the application we’re designing (or redesigning) relate to the convergence of the publishing, broadcasting, and computing industries? How does it take advantage of text, rich media, and interactivity? And how does it connect with network services, social networks, and the physical world? Where does integration yield innovation, difference, and value?
Let’s look at an example. What does convergence means for e-books?
Books as digital text: No more stacks of atoms means portability.
(books + handheld reader)
Books as multi-media: Don’t just tell me; show me.
(books + photos, videos, animation, and sound)
Books as interactivity: Tell me more or tell me less; let me try it myself.
(books + games, simulations, linking, and glosses—parallel texts)
Books as services: Access on demand, integration with other systems.
(books + continuous updating, expert sources, etc, e.g. Lexis-Nexis)
Books as social nodes: Conversation topics and learning from others.
(books + online social networks—shared interests, notes, highlights)
Books as places: The reader device becomes a window on a virtual overlay of the physical world providing details and explanations on demand.
(books + objects in the environment, e.g. contents, instructions, history, provenance)
Taking a service-design perspective, we may consider the experience cycle in relation to convergence. Imagine a matrix with steps in the customer journey along the y axis and the six elements of convergence on the x axis. What goes in each cell? What’s the message at this touch-point? What’s best delivered through images, sound, and motion? What interactions are appropriate? Can we gamify? What network services are needed? What are the social components? How can we connect to the physical world? The resulting matrix reframes the business-unit or channel focus of traditional service blueprints, substituting a focus more suited to the emerging digital environment.
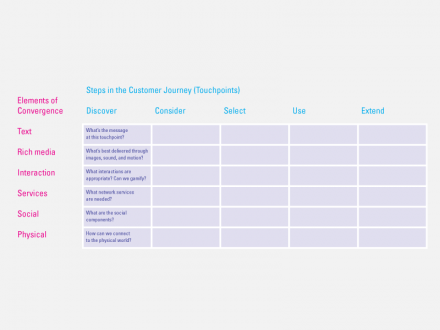
The elements of convergence provide a checklist of options to consider when assessing each step in the customer journey.
Negroponte’s convergence model was a brilliant piece of foresight. The early work of the MIT Architecture Machine Group (a precursor to the Media Lab) enabled him to predict the convergence of publishing, broadcasting, and computing. As a result of convergence, we no longer think of computing only in terms of text; we design with multimedia in mind. Communication is no longer one way; we design with interaction in mind.
But today, it’s not possible to find commercial examples of stand-alone interactive multimedia. Instead, we find it deeply embedded in networks. We find networks increasingly reliant on networked services. We find services deeply intertwined with social elements. And, of course, we find all these things embedded in the physical world. We find Convergence 1.0 deeply embedded in Convergence 2.0. We design with interactive multimedia + service + social + physical in mind.
Read Cooper Hewitt Museum Director Bill Moggridge’s Blog Post on “Convergence 2.0.”
4 Comments
Sharon Lourdes
Sep 25, 2011
11:55 am
thanks for this execellent article. Apt timing given the rise of collaborative consumption sites (Airbnb etc) 🙂
Markus
Apr 20, 2012
2:02 am
excellent!!
thx for this great piece of work!
PVS
Aug 27, 2012
5:27 am
well defined and structured. Thanks
Tony Deyal
Aug 18, 2015
12:19 am
Great article – what about Convergence.3? Is is happening, did it happen, will it take place? If so, what would be added, subtracted or multiplied? (Divided even?)